At the pinnacle of your existence lies the often overlooked crown of head. But did you know this seemingly insignificant area is important for your overall well-being?
In this informative article, we dig into everything you need to know about the crown of your head. From its anatomical significance to its role in energy flow and spiritual practices, it embraces a holistic understanding beyond the physical.
Unlock the secrets of the crown of your head and elevate your mind, body, and spirit to new heights. Are you ready to begin this enlightening journey?
Bone and Muscle Structure
1. Skull
The skull is the structure that encases and protects the human brain. The crown of the head is primarily formed by the parietal bones, which meet at the top, known as the sagittal suture. Understanding the skull's composition is crucial in various contexts, such as diagnosing skull fractures or studying bone mass changes in the modern human species.
2. Scalp

The scalp, the soft tissue covering the skull, is vital for having healthy hair follicles and supporting overall hair health.
It consists of several layers, including the skin, subcutaneous tissue, a layer of connective tissue known as the galea aponeurotica, and the periosteum, the outermost layer of the bone. A healthy scalp is essential to prevent issues like thinning hair and receding hairline.
3. Hair
Hair follicles embedded in the scalp are responsible for hair growth on the crown of the head. Maintaining healthy follicles is crucial to stimulate hair growth and prevent hair loss or thinning. The texture and density of hair can vary among individuals, particularly in the frontal and parietal regions of the scalp.
4. Muscle
Several muscles are associated with the crown of the head, including the occipitofrontalis muscle, which plays a role in facial expressions and scalp movement. These muscles can impact the appearance of the frontal region and mid-scalp, influencing factors like hair positioning and expression.
5. Blood Vessels
The artery of the external carotid artery supplies the scalp with blood, which nourishes the scalp and healthy follicles, supporting their function and hair regrowth.
6. Nerves
Nerves innervate the scalp, providing sensation to the skin, including the frontal and parietal bones. The trigeminal nerve, specifically its branches like the ophthalmic and maxillary nerves, is responsible for sensory innervation of the crown of the head.
7. Connective Tissue
Connective tissue within the scalp helps anchor the hair follicles and is key to preserving the structural integrity of the skull, and it expands in the modern human species.
Understanding the anatomy of the crown of the head is valuable for diagnosing and addressing various scalp and hair-related conditions, including receding hairline, thinning hair, and preserving the overall health of the human head.
Common Conditions and Injuries Affecting the Crown of the Head
1. Alopecia

Alopecia is a general word for hair loss. It happens when you begin to lose hair from your scalp or other parts of your body for various reasons, including:
- genetics
- hormonal changes
- autoimmune conditions
- underlying medical issues
In this condition, there is a hereditary predisposition to hair follicles becoming sensitive to androgen hormones, leading to gradual hair thinning, particularly at the crown of the head.
- Androgenic Alopecia/ Androgenetic Alopecia: Commonly known as male-pattern baldness (male-pattern hair loss) or female-pattern baldness, it is the most prevalent form of hair loss, influenced by genetic and hormonal factors.
- Alopecia Areata: A condition that results in sudden, smooth, round patches of hair loss. It can advance to total scalp hair loss, also called alopecia totalis) or total body hair loss (alopecia universalis).
- Cicatricial Alopecia (Scarring Alopecia): It destroys hair follicles and replaces them with scar tissue. Conditions like lupus or lichen planopilaris can lead to inflammation and irreversible hair loss.
- Traction Alopecia: Caused by repetitive pulling or tension on the hair, often due to tight hairstyles. Hair loss occurs in areas where the hair is frequently pulled.
- Trichotillomania: A psychological disorder that makes people feel the need to pull out their hair, often to the point of bald patches, leading to noticeable hair loss.
- Anagen Effluvium: Results in the sudden loss of hair during the anagen (growth) phase, often induced by exposure to chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
2. Dermatitis
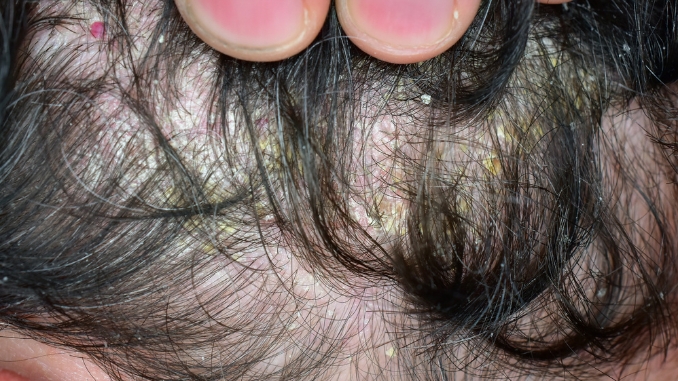
Dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin, specifically affecting the scalp. It is characterized by redness, itching, and flaking of the skin. Factors such as stress, genetics, and environmental conditions can contribute to its onset.
- Contact Dermatitis: An inflammatory skin reaction resulting from contact with irritants or allergens. Irritant contact dermatitis is caused by direct exposure to irritating substances, while allergic contact dermatitis is an immune response to allergens.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: A common and chronic form of dermatitis affecting areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp and face. It can cause redness, itching, and flaking of the skin.
- Nummular Dermatitis (Discoid Eczema): Characterized by round or coin-shaped lesions on the skin. It often presents with itchy, red, and scaly patches and may be triggered by factors such as dry skin, irritants, or stress.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: A type of eczema that affects the hands and feet, causing small, itchy blisters. It is often associated with sweating or exposure to allergens.
3. Folliculitis
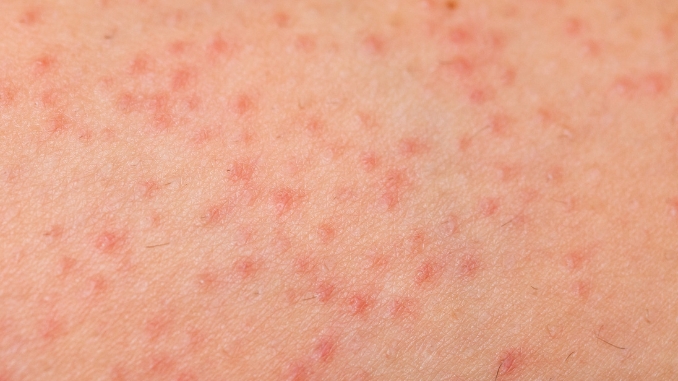
Folliculitis is the inflammation of follicles, which can lead to the formation of red, pimple-like bumps. These bumps may be itchy and uncomfortable. Folliculitis on the crown can result from bacterial or fungal infections. Poor hygiene, excessive sweating, or compromised immune function may increase the risk of developing folliculitis.
- Bacterial Folliculitis: Caused by bacterial infections, typically Staphylococcus aureus. It can result in red, pimple-like bumps around follicles on the crown.
- Fungal Folliculitis: This condition is caused by various fungi, such as Candida or dermatophytes, and leads to red, itchy bumps around hair follicles on the crown.
- Pityrosporum Folliculitis: This is caused by the yeast-like fungus Malassezia, and it results in inflamed follicles. It may be observed on the crown and other areas of the scalp.
4. Psoriasis
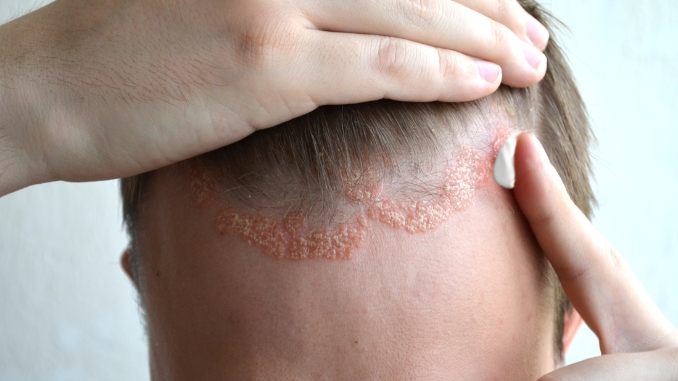
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that accelerates the skin cell turnover, developing thick, scaly plaques. When this condition affects the scalp, it can cause redness, itching, and the formation of silvery scales. The crown area may be particularly prone to psoriatic involvement, which can significantly impact the quality of life.
5. Tinea Capitis
Tinea capitis is a fungal scalp infection predominantly seen in children but also adults. It can cause hair loss, scaling, and itching.
The crown is one of the common regions affected by tinea capitis. Fungal spores invade the hair shafts, leading to inflammation and subsequent hair damage. Antifungal medications are typically used to treat this condition.
- Favus: Favus is a severe and chronic form of tinea capitis. It is characterized by the formation of yellow, cup-shaped crusts on the scalp. The crusts can lead to scarring and hair loss, and the infection may involve the crown.
- Microsporum audouinii Infection: Tinea capitis caused by Microsporum audouinii can lead to circular patches of hair loss with broken-off hairs at the scalp surface. The infection may also affect the crown and other areas of the scalp.
You might be a victim of at least one of these conditions but do not worry because we got you covered. We provided you with general tips to maintain a well-nourished crown of head.
Hair Growth Cycle and the Role of the Crown of the Head

The hair growth cycle is a continuous and natural process that follicles undergo. It consists of several phases, each with its characteristics. Here's an overview of the cycle:
1. Anagen Phase
This is the rapid stage of follicles. During the anagen phase, cells in the hair bulb divide rapidly, producing new hair.
During this phase, hair can grow at about half an inch (1.25 cm) per month. The amount of time a hair stays in the growth phase (anagen) differs among people, but it typically lasts between 2 and 7 years. The longer the anagen phase, the longer your hair can grow.
2. Catagen Phase
After the anagen phase, the follicles enter a transitional phase called catagen. This is a short phase, lasting around 2 to 3 weeks. During catagen, the hair follicle shrinks, and hair growth stops. The hair separates from the blood supply and becomes what is known as club hair.
3. Telogen Phase
During the telogen phase, also known as the resting phase, hair follicles are inactive for 3 to 4 months. At any given time, roughly 10-15% of your hair is in this resting phase. The old hair is retained during this period, but new hair forms beneath it.
4. Exogen Phase
Some sources include an additional phase known as exogen, which is the shedding phase. The old hair is shed during exogen to make way for new hair. This phase overlaps with the early part of the anagen phase, when new hair begins to grow.
The cycle is a continuous and cyclical process, with individual follicles at different stages at any given time. Factors such as genetics, hormones, age, diet, and overall health can influence the duration and effectiveness of each phase, leading to variations in its growth patterns among individuals.
Understanding the cycle is important for managing hair health and addressing hair loss or thinning issues.
Natural Remedies for Crown of Head Issues
Natural remedies can complement traditional treatments for the crown of head issues. Here are some natural remedies that may help promote scalp health:
- Tea Tree Oil - This is popularly known for its antibacterial and antifungal properties. It can be diluted with oil, such as coconut oil, and massaged onto the scalp to manage issues like dandruff or fungal infections.
- Aloe Vera Gel - Aloe vera has soothing and anti-inflammatory properties. Applying fresh aloe gel directly to the scalp may help alleviate irritation and reduce inflammation.
- Coconut Oil - Coconut oil is a popular natural moisturizer. Warm coconut oil can help hydrate dry skin and reduce flakiness. Leave it on for some time before washing it off.
- Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV) Rinse: Apple cider vinegar with water can be used as a scalp rinse to help balance the pH, reduce dandruff, and clarify the scalp. Mix one part ACV with one part water and use it after shampooing.
- Rosemary Oil - Rosemary oil is believed to regrow hair and improve circulation. Add a few drops of carrier oil, then use your fingertips to massage it into your scalp.
- Lemon Juice - Lemon juice has natural astringent properties. Dilute lemon juice with water. Apply it to the scalp to help control excess oil and dandruff.
Maintaining a healthy crown of head is essential since it highlights a multifaceted significance in physiological and cultural contexts.
Why Keep the Crown of the Head Healthy?

The crown of the head holds significant importance for various reasons, encompassing both functional and cultural aspects:
Protection of the Brain
The primary physiological importance of the crown of head, comprising the frontal bone, parietal bone, and other cranial structures, lies in its role in protecting the brain.
The skull, formed by the bones at the crown, acts as a sturdy casing that shields the delicate brain from external impacts, such as penetrating skull fractures and injury. Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI is used to evaluate the degree of damage and diagnose health conditions in cases of head trauma.
Support for Sensory Organs
The crown houses important sensory organs, including the eyes, ears, and parts of the nose. These organs play crucial roles in perception and communication, and their positioning at the crown facilitates their functions.
Hair and Growth Aesthetics
The crown of the head is a prominent location for hair growth. Hair is important to personal identity, expression, and beauty in many cultures. Individuals experiencing further hair loss in the crown often seek hair transplant procedures.
The crown's appearance, including hairstyles and hair health, can have cultural and social significance.
Expression of Emotions
Facial expressions and emotions are often manifested through movements and contractions of the muscles around the crown of the head. For example, furrowing or raising the eyebrows can convey various emotions.
Symbolism in Culture and Religion
The crown of the head holds symbolic significance in various cultures and religions. It is associated with wisdom, authority, spirituality, and divinity. Crowns or head coverings are often used as leadership or religious significance symbols.
Identity and Recognition
The crown of the head is a unique and identifiable part of an individual's anatomy. It is common to recognize someone by their hairstyle, facial features, or head shape, and the crown plays a role in personal identification.
Cultural and Traditional Practices
Hairstyles, head coverings, and grooming practices related to the crown of the head are often influenced by cultural, religious, or traditional norms. These practices can vary widely and may hold specific meanings within different communities.
Accupuncture Points
In traditional Chinese medicine and other therapeutic practices, certain acupressure points on the crown are believed to be associated with overall well-being. Stimulating these points is thought to have therapeutic effects.
Final Points
Caring for the crown of your head is more than tending to hair; it's about nurturing a crucial part of your overall well-being. From shielding the brain to housing sensory organs, this area demands attention.
Maintaining a healthy crown involves a blend of proper hygiene—regular cleansing, gentle care with suitable products—and a holistic lifestyle—nourishing nutrition, hydration, stress management, and protective measures against environmental stressors.
Embrace scalp massages, consider natural remedies, and seek professional guidance for personalized care. By treating your crown with mindfulness, you sustain healthy hair and uplift your mind, body, and spirit to their fullest potential.
You don’t have to settle for dry, damaged hair or suffer from the emotionally devastating effects of hair loss. The Master Guide to Healthy Hair provides you with all of the information you need to protect your hair and leave you with the healthy, luscious locks you’ve always dreamed of. Purchase your copy today!