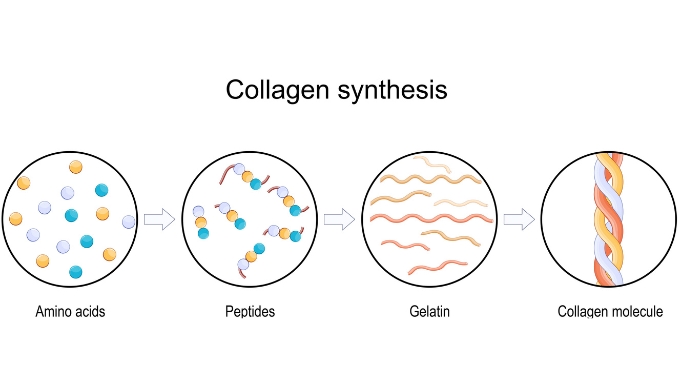
Discover the power of peptide therapy to boost your body's natural healing and speed up recovery. This treatment uses peptides, short chains of amino acids, for tissue repair and immune support.
This will explain how peptide therapy reduces inflammation, enhances healing, and improves overall well-being. Learn about different peptides, their benefits, and the science behind them.
What is Peptide Therapy?
Peptide therapy uses synthetic peptides that mimic or enhance natural peptides' functions to target specific cellular processes. The treatment leverages natural cell signaling pathways to improve overall health and physiological functions.
Moreover, peptide therapy covers various medical fields, including growth hormone enhancement, weight management, skin and joint health, and immune system support.
Research on peptide drugs focuses on creating effective treatments with minimal side effects. Approved peptide drugs treat conditions like metabolic disorders, osteoporosis, and certain cancers, showcasing their versatility in medicine.
Exploring the Diversity of Peptides: Types and Functions

Peptides can be classified by their length, function, source, or how they are made. Here is a summary of the different types of peptides.
1. Oligopeptides
Oligopeptides, with fewer than 20 amino acids, are vital in biological processes. Glutathione, a tripeptide, is a key antioxidant protecting cells from oxidative stress. These small chains play crucial roles in cellular defense, are quickly synthesized, and act immediately, essential for cellular health and resilience.
2. Polypeptides
Polypeptides are amino acid chains (20-50 units) bridging small peptides and proteins. They act as protein precursors, crucial in synthesis and folding for biological functions.
Their length also allows complex folding, enabling diverse roles like enzymatic activity and structural support essential in protein biosynthesis.
3. Neuropeptides
Neuropeptides act as crucial messengers in the nervous system, modulating pain, social bonding, and reproduction. Examples include substance P and oxytocin.
They link neural communication with behavior and physiology, highlighting their role in maintaining homeostasis and responding to environmental cues, underscoring their importance in neural pathways.
4. Hormonal Peptides

Hormonal peptides, like insulin, are biochemical messengers crucial for body functions, traveling through the bloodstream to organs.
They regulate growth, metabolism, reproduction, and other vital processes, illustrating the hormonal system's dependence on peptide signals for coordinated function and highlighting their pivotal role in health and disease.
5. Antimicrobial Peptides
Antimicrobial peptides, key to the innate immune system, defend against bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Defensins disrupt microbial membranes, protecting against infections and regulating immune responses.
Their broad-spectrum activity and immune modulation also highlight their potential in treating antibiotic-resistant infections and balancing microbial flora.
6. Ribosomal Peptides
Ribosomal peptides are produced by ribosomes in cells, based on DNA's genetic code. They include hormones and neuropeptides, crucial for various physiological functions.
This synthesis highlights the direct link between genetic information and biological molecules, emphasizing ribosomes' central role in regulating metabolism and cell communication.
7. Nonribosomal Peptides
Nonribosomal peptides are made by enzyme complexes, not ribosomes, allowing for complex structures like vancomycin.
This method includes unusual amino acids, increasing chemical diversity, and biological activity. Their vast therapeutic potential offers new drug development avenues for tough diseases.
8. Peptidomimetics
Peptidomimetics offer better stability, bioavailability, and effectiveness. Crucial in drug development, they also target biological pathways with precision and fewer side effects.
By altering natural peptide structures, peptidomimetics overcome rapid degradation, making them valuable for creating new therapeutics.
9. Cosmetic Peptides
Cosmetic peptides, like copper peptides and palmitoyl pentapeptide-3, promote collagen production, reduce wrinkles, and enhance skin barrier function.
They improve skin health and appearance by influencing collagen synthesis and repair processes. They also offer a non-invasive, biotech-driven approach to achieving youthful, healthy skin.
10. Dietary Peptides
Dietary peptides, found in foods and supplements, benefit health by improving heart health, immune function, and digestion. Casein peptides from milk, for instance, have antihypertensive properties.
These bioactive peptides highlight the potential of food-derived compounds in promoting health and preventing disease, underscoring diet's role in well-being.
The Science Behind Peptide Therapy
Peptide therapy targets specific receptors in the body, altering cell signaling and gene expression to promote health benefits like tissue regeneration, immune regulation, hormonal balance, and also cognitive improvement. Its precision minimizes side effects, making it a safe, effective choice for health optimization and performance enhancement in personalized medicine.
A new peptide-based immunotherapy[¹], detailed in Allergo Journal International by Tonti and Larché, treats allergies with 4 to 8 intradermal injections, targeting allergen-specific T cells with synthetic peptides.
This approach reduces treatment time and side effects, improves symptoms, and also maintains efficacy for at least two years, offering a promising allergy management alternative.
Moreover, advancements in peptide drug development, like peptide cyclization, enhance stability, bioavailability, and efficacy.
Cyclic peptides resist enzymatic degradation, offering longer action and greater therapeutic potential. This therapy stimulates natural growth hormone production, proving useful in age management, sports medicine, and injury recovery.
For Healing and Recovery
Peptide therapy is popular for speeding up healing and recovery, especially after sports injuries or surgery. BPC-157 helps repair tendons, ligaments, and soft tissues while reducing swelling and pain. TB-500 aids tissue repair, muscle growth, heart function, and wound healing, making it effective for recovery.
There is an article from Infusion Health[²] that claims the same. Peptide Therapy is really helpful. It uses special proteins called peptides, like BPC-157 and TB-500, which are known to help muscles grow and heal faster from injuries. These proteins are also great at fixing hurt muscles and making them stronger.
For Optimizing Health and Performance
Peptide therapy helps slow aging and also boost health. Peptides in this therapy make our bodies act younger and healthier by encouraging hormone production.
As we age, our hormone levels drop, leading to fatigue, weight gain, and other aging signs. Peptides stimulate our bodies to produce more hormones, helping us feel energetic, manage weight, and maintain strong muscles.
Peptides also improve skin by promoting collagen production, which keeps skin tight and smooth, reducing wrinkles. In essence, peptide therapy uses amino acid sequences to balance hormones, enhance skin health, and strengthen muscles, making us feel and look younger.
Peptide Therapy for Anti-Aging and Wellness

Aging happens to everyone, but peptide therapy can help slow it down and improve wellness. Peptides can refresh the body, help us live longer, and boost overall health.
The AgingBase article highlights peptide therapy as a key anti-aging intervention[³]. Using small protein fragments, it promotes skin rejuvenation, muscle repair, and immune system enhancement.
Peptides improve collagen production, reduce wrinkles, and also enhance skin elasticity, offering a personalized approach to maintain youthfulness and health. It can promote anti-aging by optimizing hormone levels, which decline with age, causing fatigue, weight gain, and decreased libido.
Peptides like GHRPs and tesamorelin restore youthful hormone levels, enhancing energy, metabolism, and well-being. Collagen and copper peptides boost collagen production, improving skin elasticity and reducing wrinkles for a youthful complexion.
Are There Side Effects to Peptide Therapy?

Peptide therapy can have side effects, which vary based on the peptide, dosage, method of use, and individual health. Generally safe under medical supervision, potential side effects may include:
Injection Site Reactions
Peptide therapy can cause minor injection site issues like redness, pain, swelling, and itchiness. These are similar to small bruises that heal over time. Keep the area clean to prevent infection.
Allergic Reactions
Peptide therapy can also cause allergic reactions, ranging from mild symptoms like rashes, itching, or a stuffy nose to severe issues like breathing difficulty or swelling. It's similar to food allergies.
Systemic Reactions
Peptide therapy can cause systemic reactions like nausea, headaches, dizziness, or fatigue. These effects happen as the body adjusts to the treatment. Not everyone experiences them, and they usually improve over time as the body adapts to the therapy.
Hormonal Imbalances
Peptide therapy can disrupt hormone levels, causing fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, or sleep issues due to hormonal imbalances.
Increased Risk of Infection
Peptide therapy can also increase infection risk by altering the immune system, making it less effective at fighting germs. It's like having less vigilant bodyguards, allowing more intruders. While it aids healing and muscle growth, be mindful of signs of sickness.
Immune System Modulation
Some peptides can alter immune system activity, causing immunosuppression or an overactive response, leading to illness or allergic reactions. Like adjusting a thermostat too much, peptide therapy can also make your immune system too weak or too strong. Use it carefully to maintain a balanced immune response.
Appetite Changes
Peptide therapy can alter hunger levels, making some feel hungrier and others less hungry. These changes occur because peptides affect the body's hunger signals to the brain.
Blood Sugar Fluctuations
Peptide therapy can affect blood sugar levels, causing fluctuations that might make you feel dizzy, hungry, or shaky. This is particularly important for those with diabetes or blood sugar issues.
Always inform your doctor before starting peptide therapy so they can guide you.
Don't hesitate to talk to your physician if you notice any unusual symptoms or changes during or after treatment. They can provide guidance and also ensure your well-being throughout the process.
Foods to Avoid During Peptide Therapy
When on peptide therapy, some foods might affect how well it works or how your body responds. Recommendations vary based on the type of peptides and your health, but here are some general foods to avoid:
- High Sugar Foods: These can cause inflammation and may reduce the benefits of peptide therapy, especially if it's for weight management or reducing inflammation.
- Processed and fried foods: This can also cause inflammation, which might reduce the benefits of peptides that aim to improve healing and lower inflammation.
- Alcohol: Drinking alcohol can interfere with how peptides work and harm your liver, which is also essential for processing peptides in your body.
- High-fat foods: Especially those with saturated and trans fats, can cause inflammation and harm your health, possibly reducing the effectiveness of peptide therapy.
- Certain dairy products: If you're sensitive or allergic to dairy, it can cause inflammation, which might reduce the benefits of peptide therapy.
Foods to Eat During Peptide Therapy
Consuming a nutrient-rich diet can boost the therapy's effectiveness and improve your health. Here are some foods to include:
- Lean Proteins: Chicken, turkey, fish, and plant-based proteins help muscle repair and growth, enhancing peptide therapy for muscle building and recovery.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Packed with vitamins and antioxidants, they reduce inflammation, support immunity, and also provide essential nutrients.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and oats offer complex carbs and fiber for sustained energy and digestive health.
- Healthy Fats: Omega-3s from salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, and monounsaturated fats from avocados, olive oil, and nuts, reduce inflammation and support cell health.
- Hydration: Drink water and herbal teas. Eat hydrating foods like cucumbers and watermelon to stay hydrated and aid peptide function.
- Fermented Foods: Yogurt, kefir, and also sauerkraut support gut health, crucial for peptide absorption and effectiveness.
Conclusion: The Future of Peptide Therapy

Peptide therapy offers innovative health solutions for healing, recovery, anti-aging, and wellness by regulating cell communication and biological functions. It targets specific cellular processes, enhancing healing, well-being, and muscle growth. Understanding peptide mechanisms and proper guidance allows individuals to optimize their health and unlock their full potential with peptide therapy.
Imagine if you learned about a proven all-natural system that naturally boosts your immunity in as little as 14 days. Check out this 14-Day Immune Health Quick Start Program now!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is peptide therapy safe?
Peptide therapy is generally safe when overseen by a healthcare professional and using FDA-approved peptides. Quality and source matter; reputable peptides are safer than unregulated ones. Medical guidance is crucial due to individual health conditions and potential interactions. While promising, peptide therapy requires professional oversight to ensure benefits without adverse effects.
2. How much do peptide injections cost?
The cost of injection for peptide therapy varies widely, from $100 to $500 per month for common treatments, but specialized therapies can be more expensive. For accurate pricing, consult healthcare providers or clinics specializing in peptide therapy because they can give detailed cost breakdowns based on the specific peptides and any associated medical fees.
3. Is peptide therapy legal?
Peptide therapy is legal when prescribed by doctors and approved by health authorities like the FDA for treating health conditions. Using peptides for athletic performance or muscle growth without a doctor's advice can be illegal. Buying peptides from unregulated online shops is risky and often illegal. Always check local laws and also consult a healthcare provider.
4. Who needs peptide therapy?
Peptide therapy benefits various individuals, including:
- Aging individuals: Enhances cell growth, skin elasticity, bone density, and muscle strength.
- Athletes: Supports muscle growth, fat loss, and tissue repair, reducing recovery times and injury risks.
- Chronic injury sufferers: Aids recovery and also reduces inflammation.
- Weight management seekers: Stimulates fat breakdown, metabolism, and reduces appetite.
- Hormonal imbalance patients: Balances hormones, beneficial for growth hormone deficiency.
- Immune disorder patients: Regulates immune system, aids autoimmune conditions and infections.
- Anti-aging enthusiasts: Reduces wrinkles, enhances hydration, stimulates collagen.
- Sleep issue sufferers: Improves sleep quality and patterns.
5. Are peptides FDA approved?
FDA-approved peptides are used for hormone replacement therapy (e.g., growth hormone-releasing peptides), diabetes treatment (e.g., insulin, GLP-1 agonists), osteoporosis (e.g., Denosumab), and cancer treatment. However, many non-medical peptides, such as those for anti-aging, bodybuilding, or weight loss, are often sold as supplements and lack FDA approval.
6. Who should not get peptide therapy?
Peptide therapy can be beneficial but isn't suitable for everyone. Pregnant or nursing women, individuals with cancer or hormonal disorders, children and adolescents, and also those with autoimmune diseases should be cautious. People on medication, with allergies to peptides, or with renal or liver conditions should also consult a healthcare provider before starting peptide therapy.