Pelvic pain in men can be a confusing and frustrating experience. Though often linked to women, men experience it too, and it can take a toll on daily life. I've learned that the causes can range from prostatitis to hernias and even urinary tract infections (UTIs). Each can have its own symptoms, making it essential to identify the cause for proper treatment.
Prostatitis may cause a deep pelvic ache, along with difficulty urinating or pain during ejaculation. Hernias, on the other hand, could present more with sharp pain, especially when moving or lifting something heavy. UTIs can bring burning sensations or frequent urges to pee. Recognizing these differences is the first step toward getting the right help.
Talking to a doctor early on can improve pain management and reproductive health. It's about understanding what your body is signaling and addressing it before it worsens.
What Is Pelvic Pain In Men?

Male pelvic pain can be incredibly disruptive because it impacts such a vital area of the body. The pelvic region houses vital organs and muscles, so pain there can affect urinary function, sexual health, and movement. Sometimes, the pain strikes suddenly and sharply; other times, it lingers, hindering daily activities.
Understanding what's happening with the pelvic floor is key here. The pelvic floor is a set of muscles that support the organs in this area, like the bladder and prostate. When these muscles function poorly—whether weakened or too tight—they cause sudden pelvic pain and can trigger issues like trouble urinating or discomfort during sex.
There are a few common culprits behind male pelvic pain, including conditions like prostatitis, pelvic floor dysfunction, urinary tract infections (UTIs), inguinal hernias, and epididymitis. Knowing the symptoms of these conditions is a crucial first step in getting the proper diagnosis and treatment. Addressing the underlying cause of pelvic pain is essential for improving overall quality of life.
Common Causes Of Pelvic Pain In Men

1. Prostatitis And Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
One of the most common urologic diagnoses for pelvic pain in men is prostatitis, an inflammation of the prostate gland. Prostatitis can be categorized into several types, including acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, and chronic pelvic pain [¹] syndrome (CPPS).
2. Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
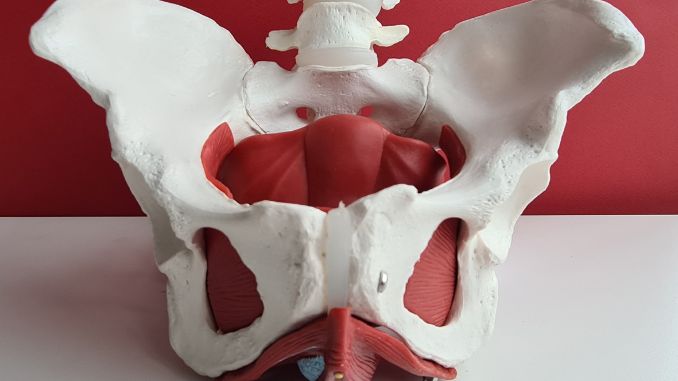
Another significant cause of pelvic pain in men is pelvic floor dysfunction. The pelvic floor muscles are crucial in supporting the pelvic organs and controlling urination and bowel movements. When these muscles become overly tight or weakened, it can lead to muscle tension and pain in the pelvic region.
Pelvic floor dysfunction can result from various factors, including physical stress, injury, or chronic conditions. The pain may be accompanied by difficulties with urination, bowel movements, and even sexual activity. Treatment often involves physical therapy to relax or strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and other pain management techniques.
3. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)

Urinary tract infections (UTIs), though more common in women, can also cause pelvic pain in men. Digestive and kidney diseases can contribute to health issues like UTIs, which often present with symptoms of pelvic discomfort. A UTI occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract, leading to infection and inflammation. Men with UTIs may experience symptoms such as bladder issues, including a frequent urge to urinate, painful urination, and lower abdominal pain.
In some cases, the infection can spread to the kidneys or prostate, causing severe pelvic pain and needing immediate medical attention. Proper diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics are essential to prevent complications.
4. Inguinal Hernia

An inguinal hernia occurs when a portion of the intestine pushes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles, leading to a bulge in the groin area. This condition can cause significant groin pain and pelvic pain in the lower abdomen in men, especially when lifting heavy objects, coughing, or straining.
Symptoms may also include a noticeable bulge in the groin, discomfort during physical activity, and lower back pain. An inguinal hernia often requires surgical repair, particularly if it becomes painful or if the hernia becomes trapped or strangulated.
5. Epididymitis

Epididymitis is inflammation of the epididymis, a tube behind the testicle that stores and carries sperm. A bacterial infection, including sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea, often causes this condition.
Men with epididymitis may experience testicular pain, swelling, and perineal pain. The condition can also cause pelvic pain and discomfort in the groin. Prompt treatment with antibiotics is crucial to prevent complications and alleviate pain.
Identifying Symptoms Of Pelvic Pain In Men
Recognizing the symptoms associated with pelvic pain in men is essential for identifying the underlying cause and seeking appropriate treatment. Irritable bowel syndrome can cause pelvic pain in men by creating symptoms along the intestinal tract that lead to pelvic discomfort. The symptoms can vary depending on the specific condition but often overlap, making a thorough evaluation necessary.
Here's a breakdown of the common symptoms that may accompany pelvic pain:
Pain Types
Urinary Symptoms
Sexual Health Issues
These symptoms often overlap, making it challenging to identify the exact cause of pelvic pain without professional evaluation. Men experiencing these symptoms must undergo diagnostic tests and consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis And Medical Evaluation
When it comes to pelvic pain in men, early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Given the complexity of the pelvic region and the variety of potential causes, a thorough medical evaluation is necessary to pinpoint the exact issue.
Here's how the diagnosis process typically unfolds:
1. Medical History And Symptom Assessment
The first step in diagnosing pelvic pain is a detailed medical history and assessment of symptoms. The healthcare provider will ask about the pain's duration, intensity, and location, as well as any accompanying symptoms such as urinary issues, sexual dysfunction, or lower back pain. Understanding the full spectrum of symptoms can help narrow down potential causes, whether it's prostatitis, pelvic floor dysfunction, or an inguinal hernia.
2. Physical Examination
A physical examination, mainly a pelvic exam, is often performed to evaluate the condition of the pelvic floor muscles and check for signs of inguinal hernias, testicular pain, or perineal pain. The doctor may palpate the abdomen and groin area during this exam to detect tenderness, swelling, or abnormal masses. For conditions like prostatitis, a digital rectal exam (DRE) might be conducted to assess the prostate gland.
3. Diagnostic Tests
Depending on the initial findings, the doctor may order several diagnostic tests to investigate the cause of the pelvic pain further:
4. Specialist Referrals
In some cases, the complexity of the condition may require referral to a specialist, such as a urologist for prostatitis or epididymitis or a physical therapist for pelvic floor dysfunction. Consulting a pelvic floor physical therapist can be crucial for managing symptoms of Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS) in men, as they can significantly improve patients' quality of life by addressing symptoms and promoting a holistic approach to treatment. Specialist evaluations can provide more targeted insights and help formulate a comprehensive treatment plan.
Importance Of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is vital to prevent complications and improve outcomes. Conditions like prostatitis or inguinal hernias can lead to more severe health issues if left untreated, while chronic pelvic pain syndrome [²](CPPS) can significantly impact the quality of life. Timely intervention can alleviate symptoms, reduce pain, and restore normal function.
Treatment Options For Pelvic Pain In Men
Treating pelvic pain in men requires a tailored approach depending on the underlying cause. Effective treatment targets both the pain and its root cause, whether it's prostatitis, pelvic floor dysfunction, or a UTI.
Here's an overview of the most common treatment options:
1. Medical Treatments
2. Physical Therapy
3. Lifestyle Changes
4. Alternative Therapies
5. Surgical Interventions
Conclusion
Dealing with pelvic pain can really disrupt everyday life. From what I’ve come to understand, identifying the cause is key to finding some relief. Different issues like prostatitis, pelvic floor dysfunction, or even a UTI can lead to pain in this sensitive area. The encouraging part is that an early diagnosis can help manage symptoms before they spiral.
It seems like having a well-rounded treatment plan makes all the difference. This could involve medical treatments, physical therapy aimed at strengthening or relaxing the pelvic muscles, or even making small lifestyle changes that can help ease the pain. I’ve realized it’s crucial not to ignore pelvic pain or hope it’ll just fade away on its own. Getting in touch with a healthcare professional early on can prevent things from escalating.
With the right approach, it’s definitely possible to manage pelvic pain. It’s really about finding a balance that lets comfort and confidence return to your daily life.
Strengthen and Support Your Core with Gentle Yoga! Discover 10 Gentle Yoga Poses for a Strong Pelvic Floor - easy, effective moves you can do anytime to build resilience and balance.